From large-scale water treatment plants in India to basic laboratory disinfection, one chemical compound stands out for its power and versatility: bleaching powder. If you’ve ever wondered about the science behind this common substance, you’ve come to the right place.
This comprehensive guide answers every key question about the **bleaching powder formula (CaOCl₂) **, its uses, chemical properties, and critical safety guidelines.
What is the Chemical Name and Formula of Bleaching Powder?
Understanding this compound starts with its core identity.
- What is the formula for bleaching powder? The correct bleaching powder formula is CaOCl₂. This molecular structure is key to its reactive properties.
- What is the chemical name of CaOCl₂? The proper chemical name for the active ingredient in bleaching powder is Calcium Hypochlorite. It’s also referred to by other names.
- What is another name for bleaching powder? You might see it called Chloride of lime or Calcium oxychloride.
- Is bleaching powder a salt? Yes, chemically it’s classified as a mixed salt of two acids: hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
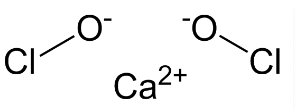
How Bleaching Powder Works: The Science of Oxidation
The effectiveness of CaOCl₂ lies in its powerful chemical reactions.
- How does bleaching powder work? The magic of the bleaching powder formula is its ability to release nascent oxygen ([O]) when it reacts with water. This single oxygen atom is a potent oxidizing agent. It breaks the chemical bonds in colored molecules (chromophores), making them colorless, and destroys the cell walls of pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
- Why does bleaching powder smell of chlorine? That distinct, sharp smell is chlorine gas being released. When **bleaching powder (CaOCl₂) ** is exposed to moisture and carbon dioxide in the air, it slowly decomposes, producing this smell. This is a sign of its active nature.
- Is bleach a base or acid? When dissolved in water, bleaching powder forms a strong alkaline (basic) solution, with a pH typically ranging from 11 to 13. Understanding this is crucial for safe handling and for preventing dangerous reactions with acids.
- What is the difference between chlorine and bleaching powder? This is a key distinction. Chlorine (Cl₂) is a pure elemental gas, while bleaching powder is a solid compound that serves as a stable, easy-to-handle source of active chlorine for various applications.
Top Uses of Bleaching Powder in 2025
The uses of bleaching powder are vast, spanning industrial, commercial, and public health sectors across India.
- Water Purification: Its primary use is disinfecting drinking water and swimming pools.
- Textile Industry: It is widely used for bleaching cotton and linen fabrics.
- Paper Industry: Used to bleach wood pulp.
- Disinfectant: An excellent agent for sterilizing lab surfaces and equipment. For a full range of cleaning agents, see our Lab Disinfectants category.
- Stain Removal: The oxidizing action effectively removes tough stains from clothes and surfaces.
Bleaching Powder for Water: Dosage and Safety
- Can bleaching powder be used in drinking water? Absolutely. It is a cornerstone of public health for making drinking water safe.
- How much bleaching powder is in 1000 litre water? For disinfection, a standard dose is about 1-2 grams of quality bleaching powder per 1000 litres of water. This dosage can change based on water turbidity and contamination levels. Always follow official health guidelines.
Safety First: Handling CaOCl₂ Safely
Handling any chemical requires knowledge and care. Refer to our General Lab Safety Guidelines for more information.
- Is bleach harmful to skin? Yes, it is corrosive. Direct contact can cause chemical burns and severe irritation. Always wear gloves and protective eyewear.
- What are the disadvantages of bleach? Besides being a skin irritant, it can damage certain fabrics, and its fumes can be harmful if inhaled in a poorly ventilated space. Crucially, never mix bleach with ammonia or acid-based cleaners, as this creates toxic chlorine gas.
- Does bleach remove tan permanently? No, and you should never apply bleach to your skin. It will cause severe chemical burns and does not affect your skin’s natural melanin production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: What is the pH of human blood? While on the topic of pH, human blood is slightly alkaline, maintained in a very tight range of 7.35 to 7.45.
- Q2: What is bleaching and its benefits? Bleaching is a chemical process that uses an oxidizing agent to whiten or disinfect materials. Its main benefits are sterilization (killing germs) and whitening (removing color).
- Q3: Does bleach effectively remove stains? Yes, its oxidizing power is highly effective at breaking down the molecules that cause stains, making it a powerful laundry and cleaning agent.
For More Details : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium_hypochlorite

